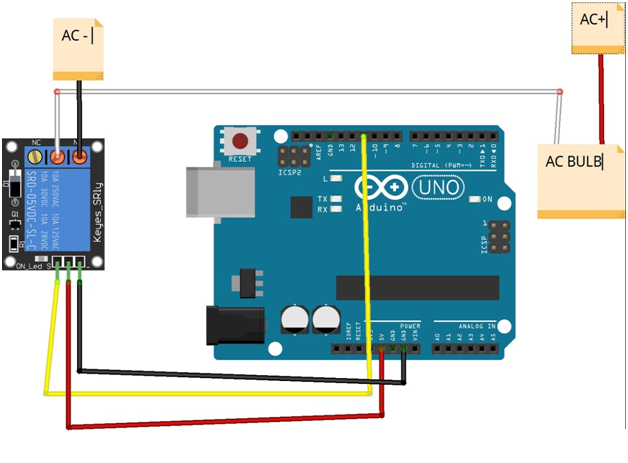
Creating position of Joy Stick program using Arduino UNO
Required Components
- Arduino UNO -1 no
- Joystick Module -1 no
- LEDs -5 no
- Resistor: 150 ohm -5 no
- Breadboard -1 no
- Connecting wires -1 set
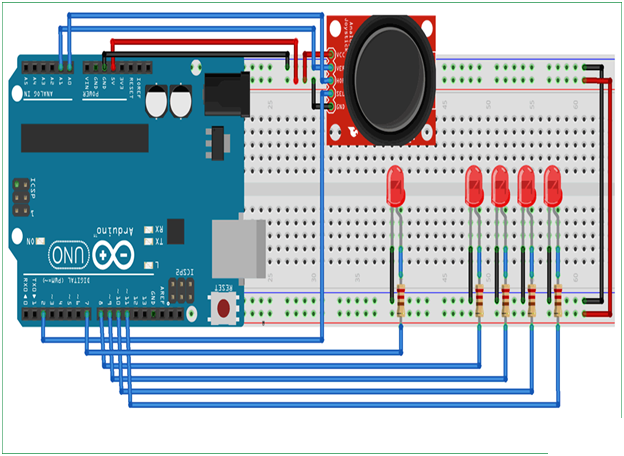
Circuit
Steps
- Make sure the components are working properly.
- Connect the 150 Ohm Resistor and Arduino Uno gnd to the LED.
- Connect the Arduino Uno Board 2nd pin to the Joy stick.
- Connect the Arduino Uno 8 ,9 ,10 ,11th pins to the Joy stick.
- Connect the Arduino Uno 5V & gnd to the Joy stick controller.
- Connect the Arduino Uno Board A0 & A1 pins to the X -axis & Y-axis.
- Check the Circuit Connections.
- Check the Arduino program.
- Run the Arduino program.
Arduino Program
int joyX=A0;
int joyY=A1;
int button=2;
int buttonState = 0;
int buttonState1 = 0;
void setup( )
{
pinMode(7,OUTPUT);
pinMode(button,INPUT);
digitalWrite(button, HIGH);
Serial.begin(9600);
}
void loop( )
{
int xValue = analogRead(joyX);
int yValue = analogRead(joyY);
Serial.print(xValue);
Serial.print("\t");
Serial.println(yValue);
buttonState = digitalRead(button);
Serial.println(buttonState);
if (xValue>=0 && yValue<=10)
{
digitalWrite(10, HIGH);
}else
{
digitalWrite(10, LOW);
}
if (xValue<=10 && yValue>=500)
{
digitalWrite(11, HIGH);
}else
{
digitalWrite(11, LOW);
}
if (xValue>=1020 && yValue>=500)
{
digitalWrite(9, HIGH);
}else
{
digitalWrite(9, LOW);
}
if (xValue>=500 && yValue>=1020)
{
digitalWrite(8, HIGH);
}else
{
digitalWrite(8, LOW);
}
if (xValue>=1020 && yValue>=1020)
{
digitalWrite(9, LOW);
digitalWrite(8, LOW);
}
if (buttonState == LOW)
{
Serial.println("Switch = High");
digitalWrite(7, HIGH);
}else
{
digitalWrite(7, LOW);
}
buttonState1 = digitalRead(7);
Serial.println(buttonState1);
delay(100);
}
Usage
- Gaming controls
- Air craft