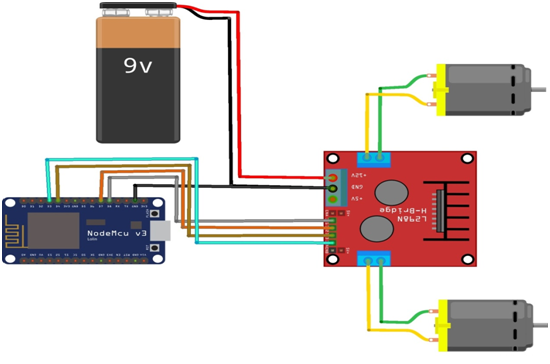
Creating 2 DC Motors control program using Node MCU
Required Components
- Node MCU -1 no
- L298N Motor Driver -1 no
- 9V Battery -1 no
- 5V DC Motor -2 no
- Motor wheel -2 no
- Cable -1 no
- Jumper Wires -7 no
Circuit
Steps
- Make sure the components are working properly.
- Connect the 5V Battery to the L298N Motor Driver.
- Connect the ENA, IN1, IN2, IN3, IN4, ENB pins to the Node MCU pins D2, D0, D1, D7, D6, D5 properly.
- Connect the DC motor pins to the motor driver output pins.
- Connect the Node MCU ground connection to the driver gnd respectively.
- Connect the Power to the NodeMCU.
- Check the Arduino program.
- Check the Circuit Connections.
- Run the Arduino program.
Arduino Program
#include <ESP8266WiFi.h>
const char* ssid = "*****";
const char* password = "*********";
int motor1pin1 = 16; //D0
int motor1pin2 = 5; //D1
int enPin1 = 4; //D2
int motor2pin1 = 13; //D7
int motor2pin2 = 12; //D6
int enPin2 = 14;//D5
WiFiServer server(80);
void setup()
{
Serial.begin(115200);
delay(10);
pinMode(motor1pin1, OUTPUT);
pinMode(motor1pin2, OUTPUT);
pinMode(enPin1, OUTPUT);
digitalWrite(enPin1, HIGH);
pinMode(motor2pin1, OUTPUT);
pinMode(motor2pin2, OUTPUT);
pinMode(enPin2, OUTPUT);
digitalWrite(enPin2, HIGH);
Serial.println();
Serial.println();
Serial.print("Connecting to ");
Serial.println(ssid);
WiFi.begin(ssid, password);
while (WiFi.status() != WL_CONNECTED)
{
delay(500);
Serial.print(".");
}
Serial.println("");
Serial.println("WiFi connected");
server.begin();
Serial.println("Server started");
Serial.print("Use this URL to connect: ");
Serial.print("http://");
Serial.print(WiFi.localIP());
Serial.println("/");
}
void loop()
{
WiFiClient client = server.available();
if (!client)
{
return;
}
Serial.println("new client");
while(!client.available())
{
delay(1);
}
String request = client.readStringUntil('\r');
Serial.println(request);
client.flush();
int value,value1 = LOW,value2 = LOW,value3 = LOW,value4 = LOW;
if (request.indexOf("/MotorForward") != -1)
{
digitalWrite(motor1pin1, HIGH);
digitalWrite(motor1pin2, LOW);
digitalWrite(motor2pin1, HIGH);
digitalWrite(motor2pin2, LOW);
delay(1000);
value1 = HIGH;
value2 = LOW;
value3 = HIGH;
value4 = LOW;
}
if (request.indexOf("/MotorBackward") != -1)
{
digitalWrite(motor1pin1, LOW);
digitalWrite(motor1pin2, HIGH);
digitalWrite(motor2pin1, LOW);
digitalWrite(motor2pin2, HIGH);
delay(1000);
value1 = LOW;
value2 = HIGH;
value3 = LOW;
value4 = HIGH;
}
if (request.indexOf("/MotorLeft") != -1)
{
digitalWrite(motor1pin1, LOW);
digitalWrite(motor1pin2, HIGH);
digitalWrite(motor2pin1, HIGH);
digitalWrite(motor2pin2, LOW);
delay(1000);
value1 = LOW;
value2 = HIGH;
value3 = HIGH;
value4 = LOW;
}
if (request.indexOf("/MotorRight") != -1)
{
digitalWrite(motor1pin1, HIGH);
digitalWrite(motor1pin2, LOW);
digitalWrite(motor2pin1, LOW);
digitalWrite(motor2pin2, HIGH);
delay(1000);
value1 = HIGH;
value2 = LOW;
value3 = LOW;
value4 = HIGH;
}
if (request.indexOf("/MotorStop") != -1)
{
digitalWrite(motor1pin1, LOW);
digitalWrite(motor1pin2, LOW);
digitalWrite(motor2pin1, LOW);
digitalWrite(motor2pin2, LOW);
delay(1000);
value1 = LOW;
value2 = LOW;
value3 = LOW;
value4 = LOW;
}
client.println("HTTP/1.1 200 OK");
client.println("Content-Type: text/html");
client.println(""); // do not forget this one
client.println("<!DOCTYPE HTML>");
client.println("<html>");
client.print("motor is now: ");
if(value1 == HIGH && value2 == LOW && value3 == HIGH && value4 == LOW ) {
client.print("Forward");
}
else if(value1 == LOW && value2 == HIGH && value3 == LOW && value4 == HIGH ) {
client.print("Backward");
}
else if(value1 == LOW && value2 == HIGH && value3 == HIGH && value4 == LOW ) {
client.print("Left");
}
else if(value1 == HIGH && value2 == LOW && value3 == LOW && value4 == HIGH ) {
client.print("Right");
}
else if(value1 == LOW && value2 == LOW && value3 == LOW && value4 == LOW ) {
client.print("Stop");
}
client.println("<br><br>");
client.println("<a href=\"/MotorForward\"\"><button>Forward </button></a>");
client.println("<a href=\"/MotorBackward\"\"><button>Backward </button></a><br />");
client.println("<a href=\"/MotorLeft\"\"><button>Left </button></a>");
client.println("<a href=\"/MotorRight\"\"><button>Right </button></a><br />");
client.println("<a href=\"/MotorStop\"\"><button>Stop </button></a>");
client.println("</html>");
delay(1);
Serial.println("Client disonnected");
Serial.println("");
}
Usage
- Drive
DC motors
- Drive
Stepping motors
- In
Robotics
Projects
- Diwa Robot